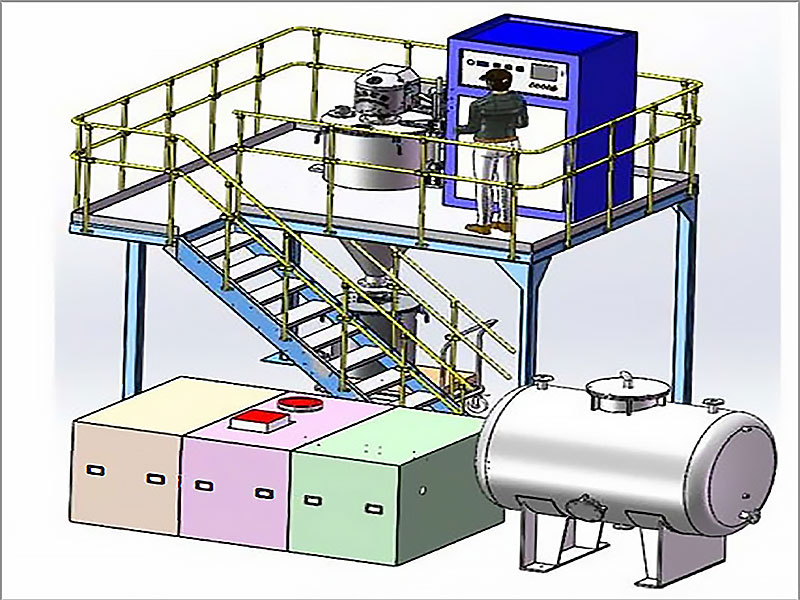
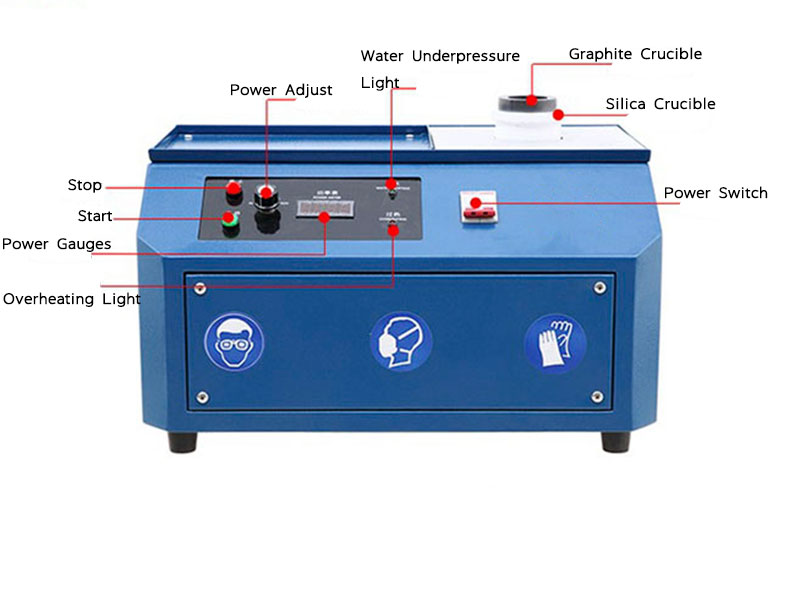
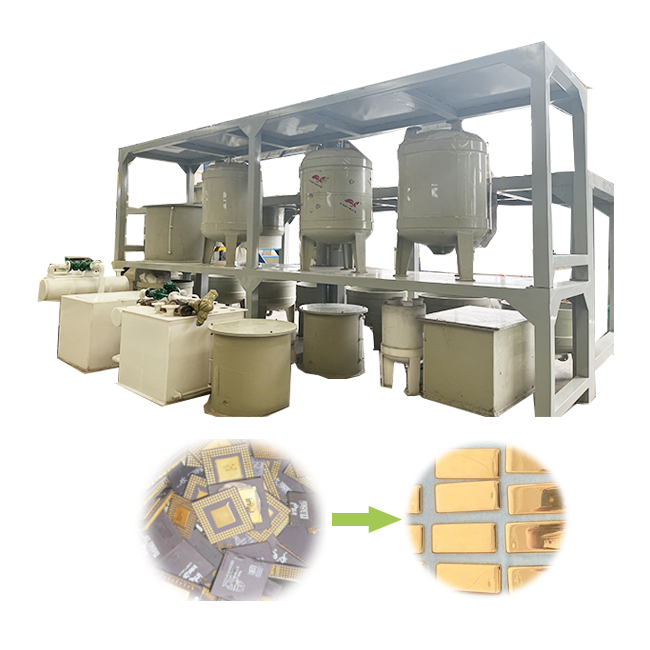
gold refining process chart


Understanding the Gold Refining Process Chart
The gold refining process is a series of chemical and physical steps that purify gold to its highest possible quality. The process involves several stages, each contributing to the removal of impurities such as silver, copper, and other base metals. A gold refining process chart can help visualize these steps, making it easier to understand how raw gold is transformed into pure, high-quality gold.
In this article, we will explore the gold refining process in detail, discussing each step and how it contributes to producing pure gold. The gold refining process chart serves as a useful tool for understanding these steps in a structured and organized way.
What is a Gold Refining Process Chart?
A gold refining process chart is a diagram that outlines the different stages involved in refining gold. It helps map out the journey of gold from its raw form to its refined state. Each step in the chart has a specific purpose, whether it’s removing impurities or enhancing the purity of the gold.
Key Components of the Gold Refining Process Chart
A typical gold refining process chart includes the following steps:
- Melting: Gold is heated to its melting point in a furnace, where it is separated from other materials.
- Chemical Treatment: Chemical solutions such as aqua regia or chlorine gas are used to dissolve impurities.
- Filtration and Precipitation: Impurities are filtered out, and gold is precipitated from the solution.
- Electrolysis: For higher purity levels, electrolysis may be used to refine the gold further.
- Smelting: The final product is smelted into bars or coins, depending on the intended use.

Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Gold Refining Process
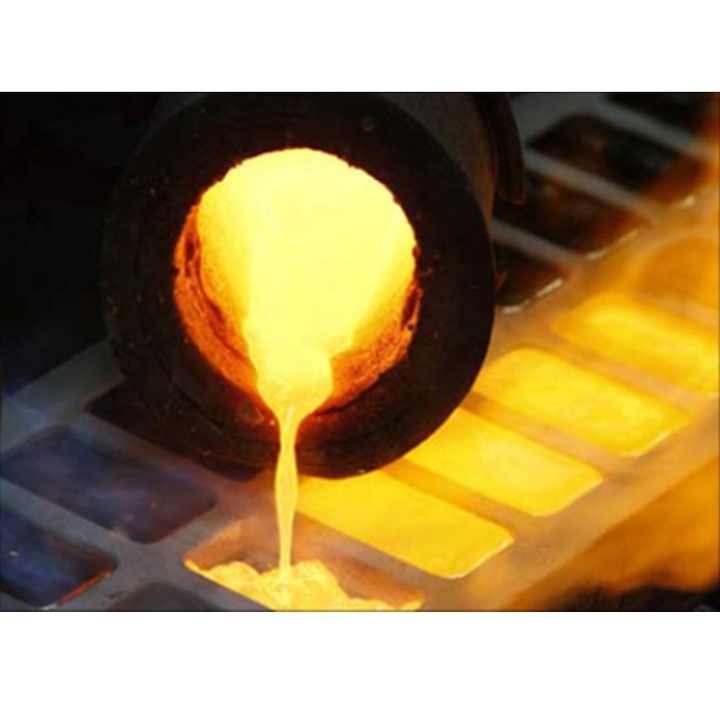
1. Melting the Gold
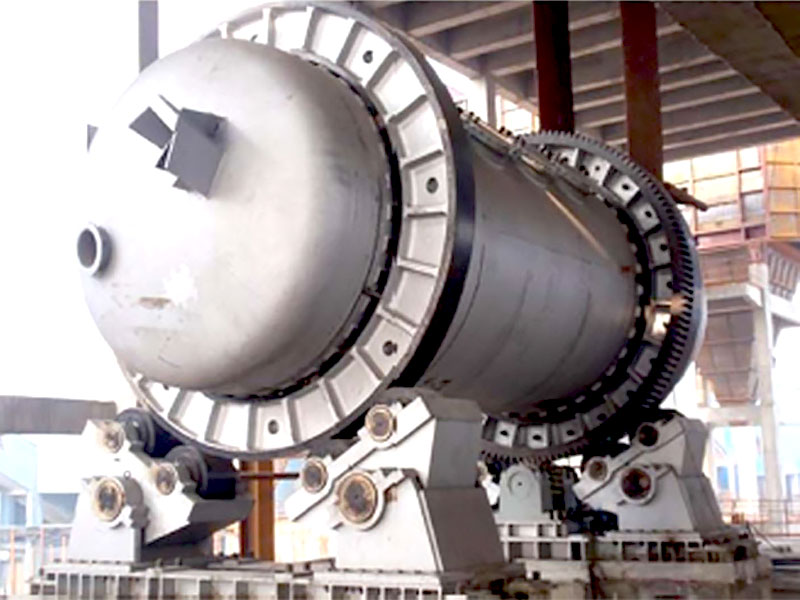
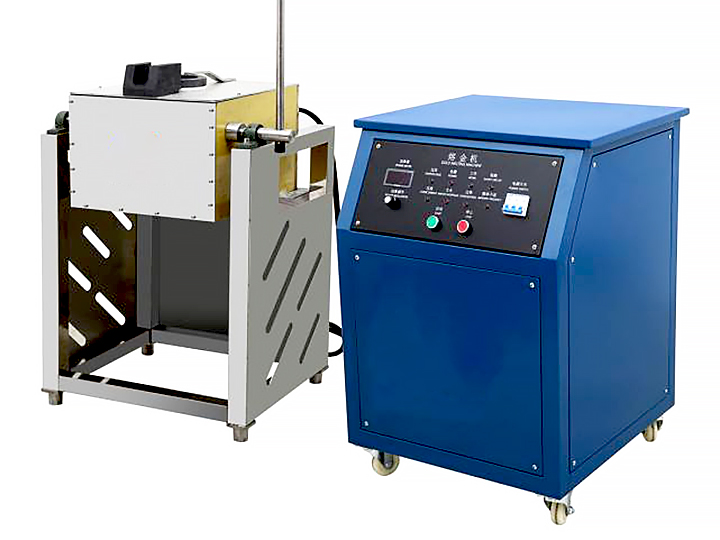
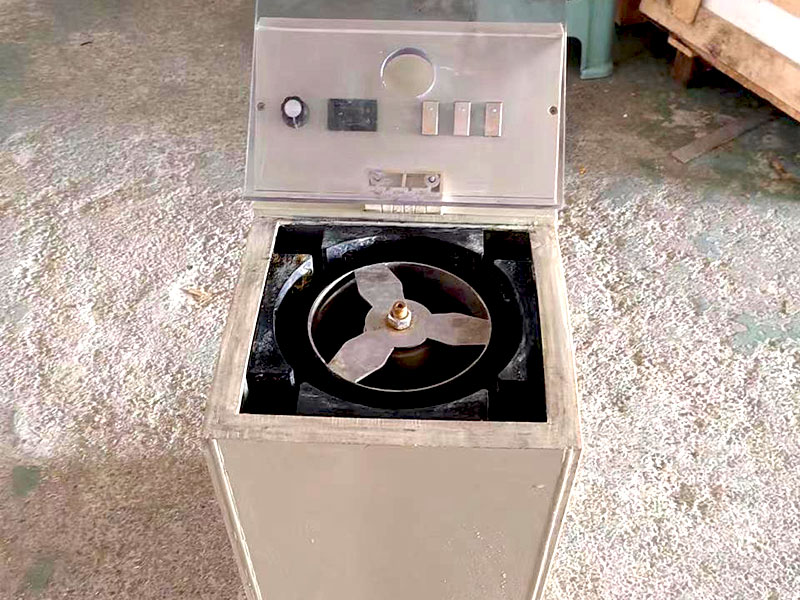
The first step in the gold refining process, as shown on the chart, involves melting the raw gold. This is typically done in a furnace at extremely high temperatures, where the gold melts and separates from non-metallic materials. The molten gold is then poured into molds to form ingots, which are easier to handle and refine further.
2. Chemical Treatment to Remove Impurities
Once the gold is melted and formed into ingots, it undergoes chemical treatment to remove impurities. The most common chemical methods are aqua regia and chlorine gas treatment. Aqua regia is a mixture of nitric and hydrochloric acids that dissolves gold, allowing impurities like silver and base metals to be separated. Chlorine gas is often used in large-scale operations like the Miller process, which quickly eliminates impurities in molten gold.
3. Filtration and Precipitation
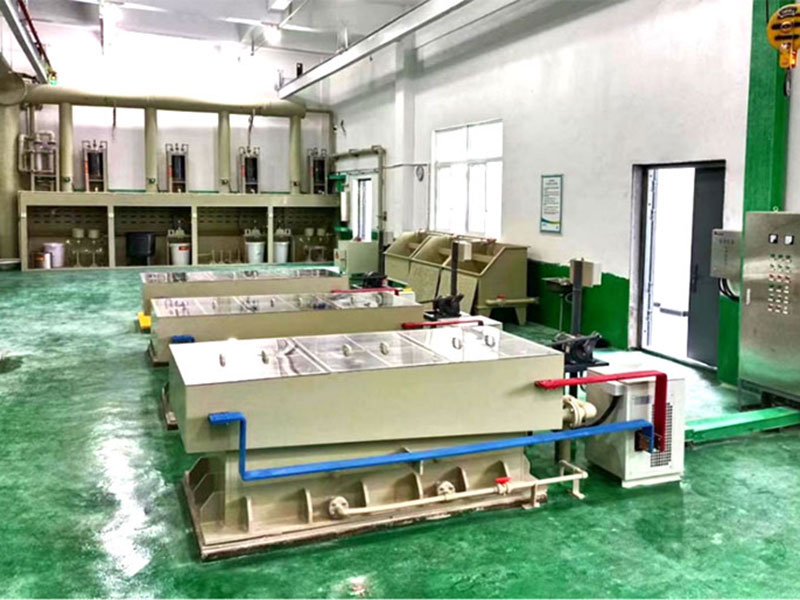
After chemical treatment, the gold solution undergoes filtration and precipitation. During this phase, impurities are filtered out, leaving behind a solution containing dissolved gold. A reducing agent is then added to the solution, causing the gold to precipitate out as solid particles. These particles are collected and prepared for further refinement.
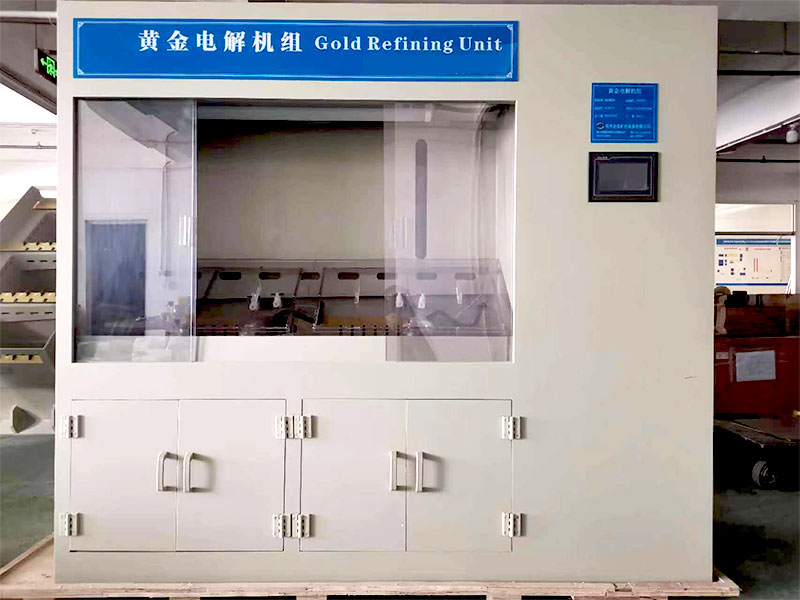
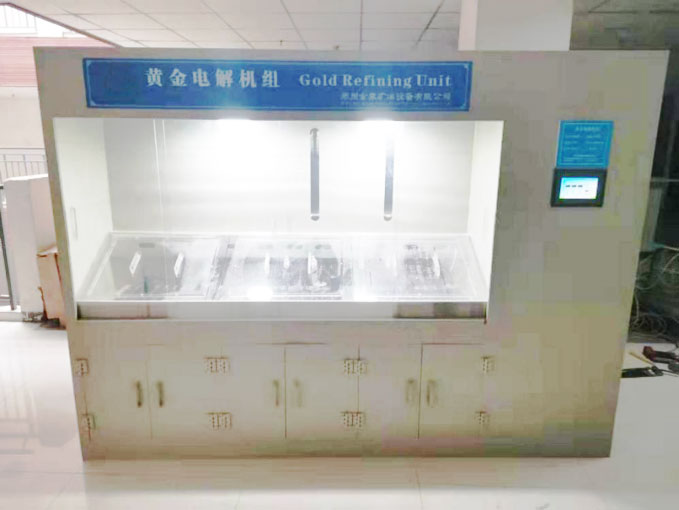
4. Electrolysis for Higher Purity
For those seeking ultra-pure gold, the process chart includes electrolysis as a final step. Electrolytic refining uses an electrical current to dissolve impure gold from an anode and deposit it onto a cathode. This method is used to achieve gold purity levels of up to 99.99%, ideal for use in industries like electronics and medical equipment.
5. Smelting and Final Product
The last step on the gold refining process chart is smelting, where the refined gold is melted and poured into molds to create bars, coins, or other products. This stage finalizes the gold’s transformation from raw ore to pure metal. Depending on the intended use, the gold may undergo additional testing to confirm its purity before being distributed for sale or industrial use.

Why the Gold Refining Process Chart is Important
The gold refining process chart is a crucial tool for anyone involved in gold refining, whether on a small or large scale. It provides a clear visual representation of each step, helping operators understand the sequence of processes and identify where improvements can be made. It also aids in troubleshooting by identifying potential bottlenecks or issues at specific stages of the process.
Benefits of Using a Gold Refining Process Chart
- Clarity: The chart simplifies complex processes, making them easier to follow.
- Efficiency: It helps streamline the refining process by identifying key steps that require attention.
- Quality Control: By following the chart, refiners can ensure that each step is completed correctly, resulting in high-quality gold.
Variations in the Gold Refining Process
While the gold refining process chart follows a general sequence, there can be variations depending on the scale and specific needs of the refining operation. For example, small-scale refiners might skip electrolysis, focusing only on chemical treatment to achieve satisfactory purity levels. Large industrial refiners may employ both the Miller process and electrolytic refining to achieve the highest possible purity in the shortest time.
Factors That Affect the Refining Process
- Type of Gold: Whether refining scrap gold or gold ore affects the methods and steps in the process.
- Desired Purity: Higher purity levels may require additional steps, such as electrolysis or multiple rounds of chemical treatment.
- Scale of Operation: Large-scale operations often use more sophisticated equipment and processes, while small-scale operations may opt for simpler methods.
The gold refining process chart provides a clear, structured guide to understanding the intricate steps involved in transforming raw gold into its purest form. From melting and chemical treatment to electrolysis and smelting, each stage is critical to ensuring the final product meets the required purity standards. By following this process chart, gold refiners can achieve high-quality results, whether refining for jewelry, investment, or industrial use.