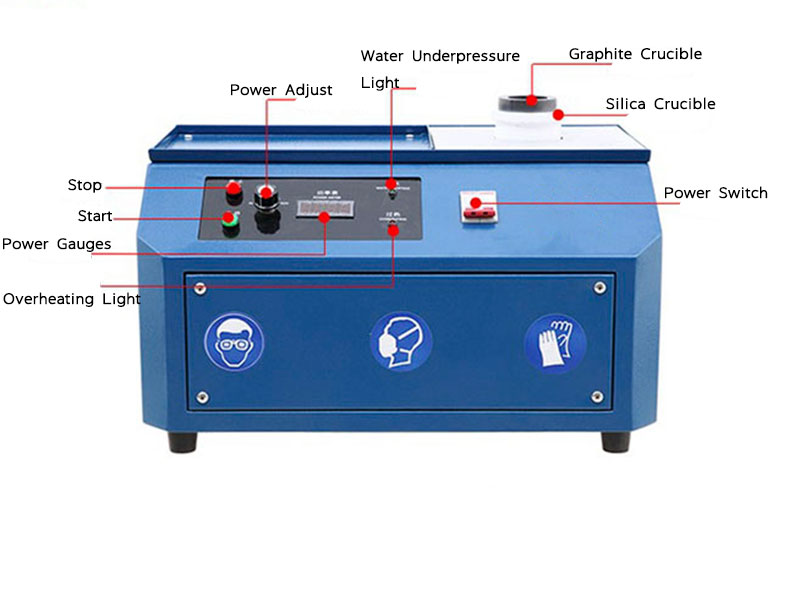
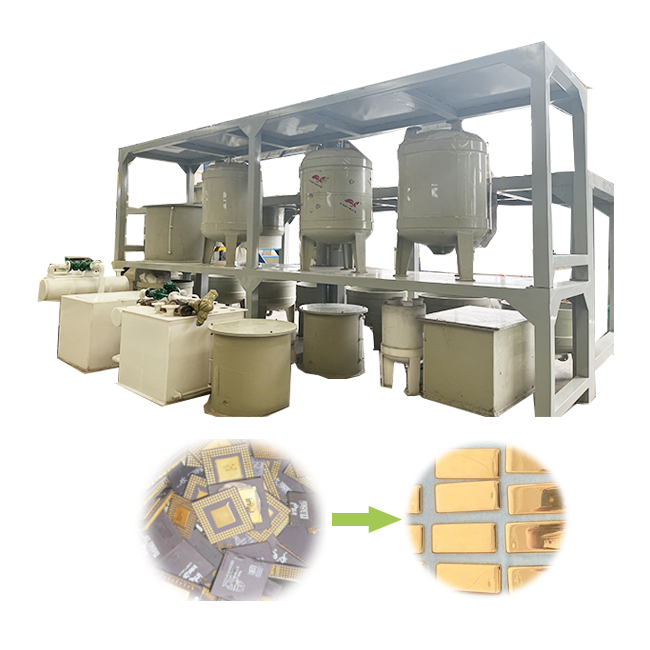
gold refining process
Understanding the Gold Refining Process: Methods, Steps, and Applications
The gold refining process is crucial for converting raw gold into a highly pure form, suitable for various industrial, financial, and commercial uses. This article delves into the different methods employed in the gold refining process, the essential steps involved, and the wide-ranging applications of the refined gold.


Methods Used in the Gold Refining Process
The gold refining process can be carried out through several methods, each tailored to achieve a specific level of purity and efficiency. The two most prominent methods are the Miller process and the Wohlwill process.
- Miller Process: The Miller process is one of the oldest and most straightforward methods of gold refining. It involves passing chlorine gas through molten gold, which reacts with impurities to form chlorides that can be easily separated from the gold. This method is quick and efficient, capable of producing gold with a purity of about 99.5%. However, it does not remove all impurities, making it less suitable for applications requiring the highest levels of purity.
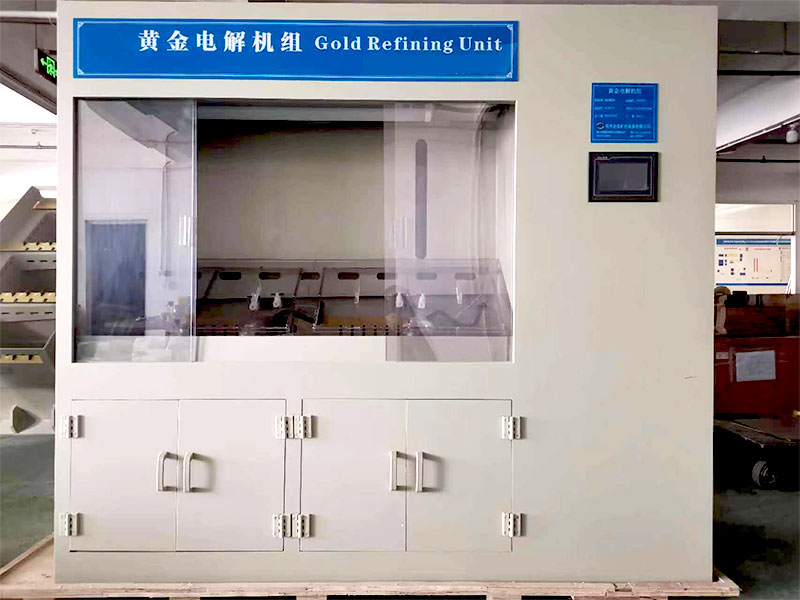
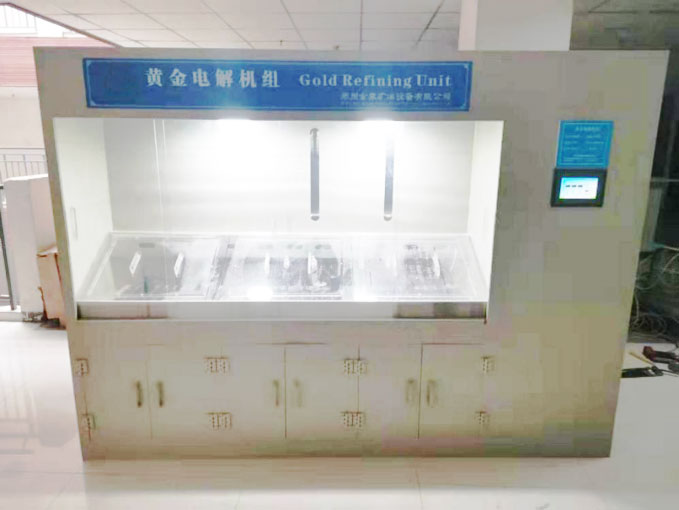
- Wohlwill Process: The Wohlwill process, developed by Emil Wohlwill in 1874, is an electrolytic refining method that yields gold of up to 99.99% purity. In this process, gold is dissolved in a solution of hydrochloric acid and gold chloride, and then an electric current is passed through the solution. This causes pure gold to deposit onto the cathode, while impurities remain in the solution or settle at the bottom. Although more time-consuming and costly than the Miller process, the Wohlwill process is essential for producing the highest quality gold.
- Aqua Regia Process: Aqua regia, a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, is another method used in the gold refining process, particularly for small-scale refining. It dissolves gold and other metals, allowing for the separation and purification of gold. This method is versatile and widely used in laboratories, but it requires careful handling due to the corrosive nature of the chemicals involved.
- Cupellation: This ancient technique is used mainly for refining gold from lead-based ores. The process involves heating the ore in a special furnace, allowing lead to oxidize and separate from the gold. While not commonly used today, cupellation remains a valuable method in certain situations where other refining techniques may not be applicable.

Key Steps in the Gold Refining Process
The gold refining process is a multi-step procedure designed to separate gold from impurities and other metals, yielding a pure and valuable product.
- Melting and Sampling: The first step in the gold refining process involves melting the raw gold material in a high-temperature furnace. This step allows for the sampling of the molten gold to determine its composition and the appropriate refining method to be used.
- Preliminary Refining: Depending on the impurities present, preliminary refining may involve the use of fluxes and other chemicals to remove base metals and other unwanted materials. This step is essential for preparing the gold for more advanced refining methods.
- Chemical Treatment: In the chemical treatment phase, the gold is subjected to acids or other chemical agents to dissolve impurities. The most common chemicals used in this step are nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, which are highly effective in separating gold from other metals.
- Electrolytic Refining: For gold that requires the highest purity levels, electrolytic refining is employed. This step involves passing an electric current through a gold-containing solution, causing pure gold to deposit onto a cathode while impurities remain in the solution. This method ensures that the final product meets the strictest purity standards.
- Filtration and Washing: After the gold has been refined, it is filtered and washed to remove any remaining chemical residues. This step is crucial for ensuring the purity and quality of the final gold product.
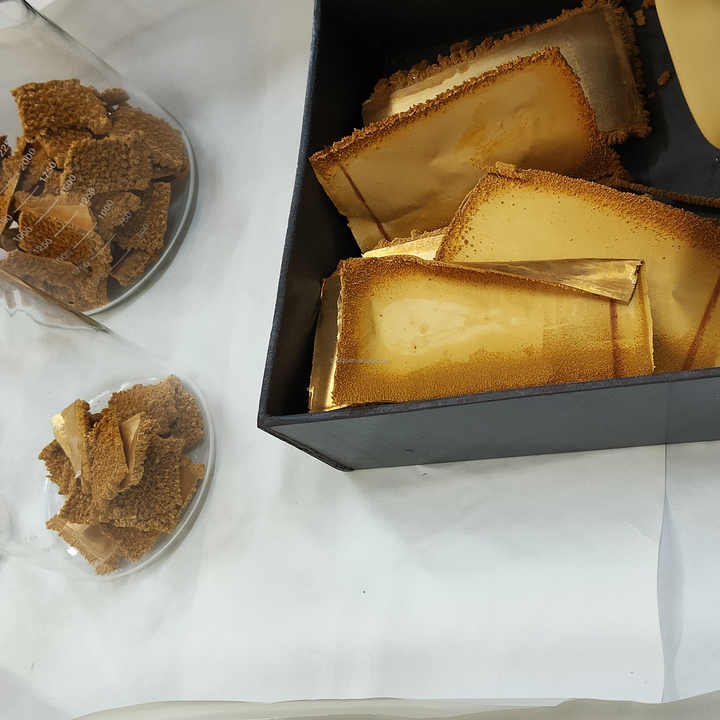
- Casting and Final Inspection: The refined gold is then melted once again and cast into bars, ingots, or other desired shapes. The final product is inspected for purity, weight, and appearance before it is ready for sale or use in various applications.
Applications of Refined Gold
The refined gold obtained through the gold refining process has numerous applications across different industries due to its high purity and desirable properties.
- Jewelry and Ornamentation: One of the most common uses of refined gold is in the jewelry industry. The high purity of refined gold makes it ideal for crafting fine jewelry, which is highly valued for its beauty, durability, and cultural significance.
- Electronics and Technology: Refined gold is widely used in the electronics industry due to its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion. It is used in the production of connectors, switches, and other components found in smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices.
- Investment and Financial Products: Gold bars, coins, and other investment-grade products are typically made from refined gold. These products are sought after by investors and central banks for their intrinsic value and as a hedge against economic instability.
- Medical and Dental Applications: Gold’s biocompatibility and resistance to tarnishing make it a valuable material in the medical field. It is used in dental work, such as crowns and bridges, and in certain medical devices and treatments.
- Aerospace and Engineering: In aerospace and advanced engineering, refined gold is used for its unique properties, including its ability to withstand extreme conditions and its effectiveness as a lubricant for mechanical parts.
The gold refining process is a sophisticated and essential practice that transforms raw gold into a highly pure and valuable material. With various methods available, from the Miller process to the Wohlwill process, refiners can achieve different levels of purity to meet specific needs. The refined gold produced through this process is indispensable in industries ranging from jewelry and electronics to medicine and aerospace. As the demand for high-purity gold continues to grow, the gold refining process will remain a vital component of the global economy.