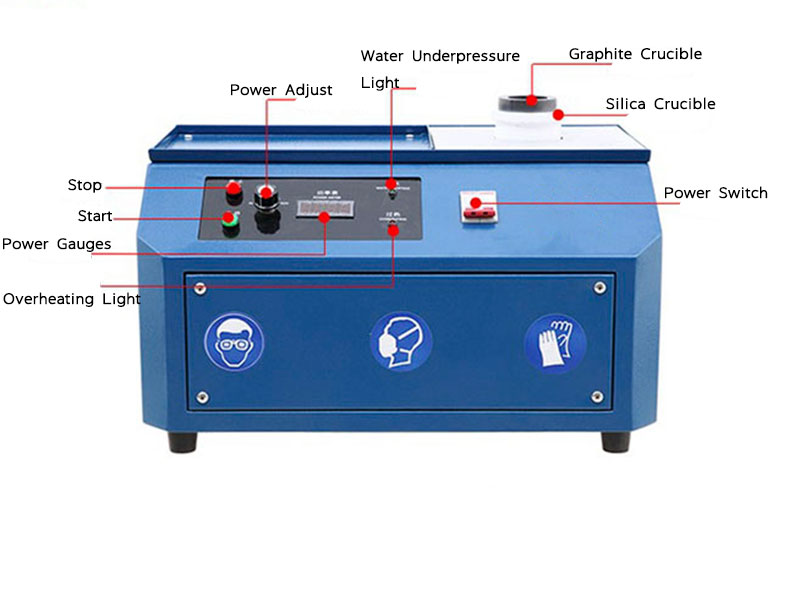
precious metal smelting process
The Precious Metal Smelting Process: A Comprehensive Overview
The precious metal smelting process is crucial for refining and purifying valuable metals such as gold, silver, and platinum. This process transforms raw ores and scrap materials into high-purity metals suitable for various applications, including jewelry, investment, and electronics. This article provides a detailed look at the precious metal smelting process, covering its key stages, equipment used, and best practices.
Understanding the Precious Metal Smelting Process
The precious metal smelting process involves several critical stages that ensure the efficient extraction and refinement of metals. Each stage plays a role in achieving the desired purity and quality of the final product.
Stages of the Precious Metal Smelting Process
- Preparation of Raw Materials
- Smelting and Refining
- Casting and Cooling
- Post-Smelting Treatments
Preparation of Raw Materials
Before the smelting process begins, the raw materials must be prepared to ensure efficient and effective processing.
Crushing and Grinding
Raw ores and scrap materials are first crushed and ground to increase the surface area and facilitate the extraction of precious metals. This step is crucial for optimizing the smelting process.
Concentration
The ground material is then concentrated to separate the valuable metals from waste materials. Various methods, such as gravity separation or flotation, may be used depending on the type of ore.
Smelting and Refining
The core of the precious metal smelting process is the actual smelting and refining stage. This is where the metals are extracted and purified.
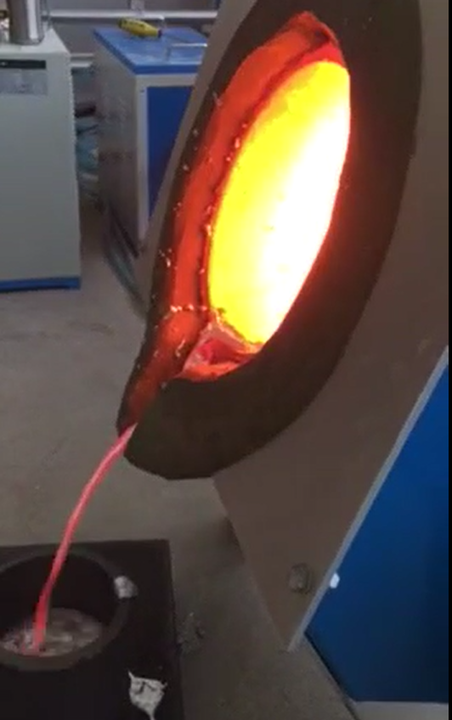
Melting
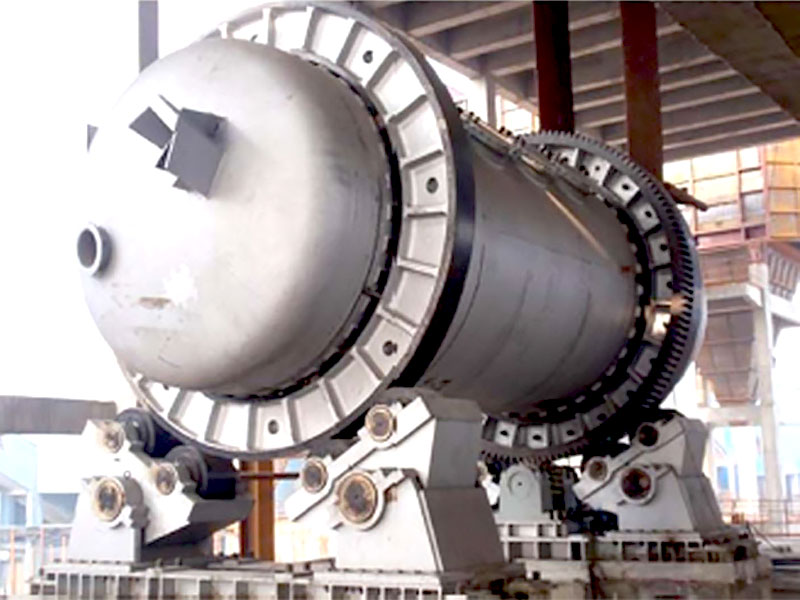
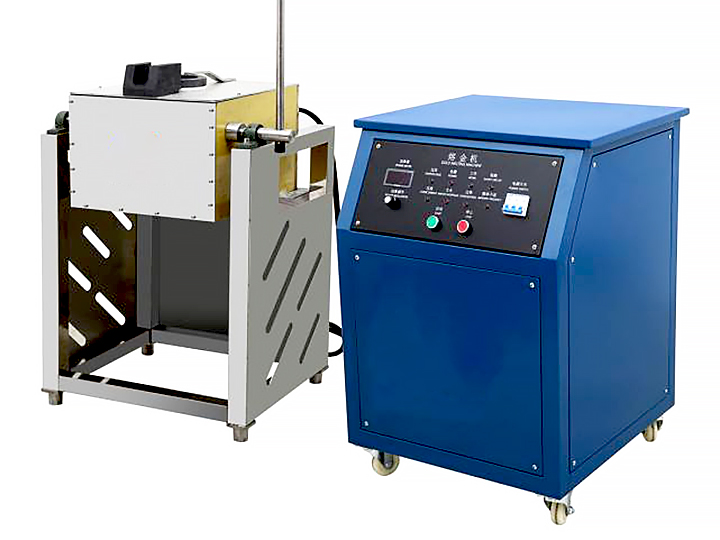
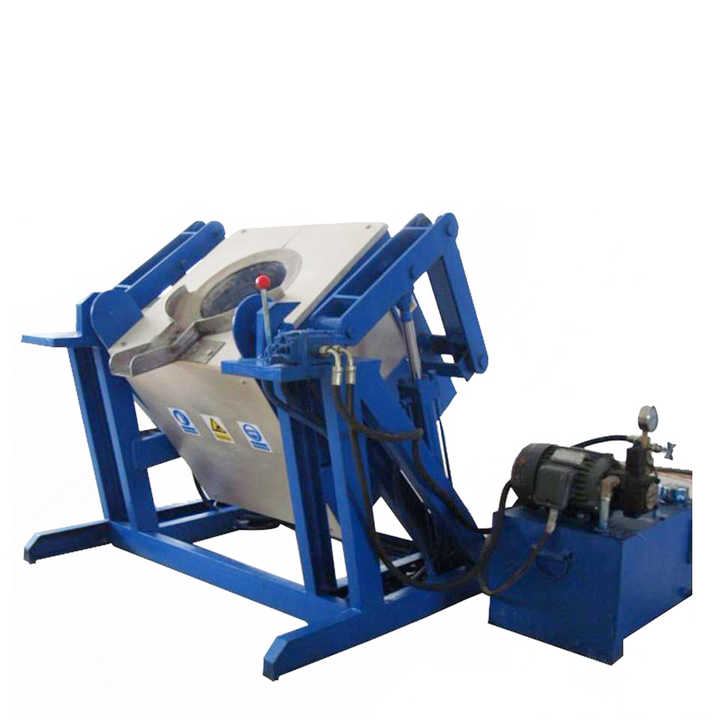
The concentrated material is placed into a smelting furnace where it is heated to high temperatures. The choice of furnace—such as an electric furnace or a blast furnace—depends on the type of metal being processed.
Flux Addition
Fluxes are added to the furnace to help separate impurities from the molten metal. Fluxes can include substances like limestone or borax, which react with impurities to form slag that can be removed.
Separation
During the melting process, impurities separate from the precious metal and rise to the surface as slag. This slag is skimmed off, leaving behind a more purified form of the metal.
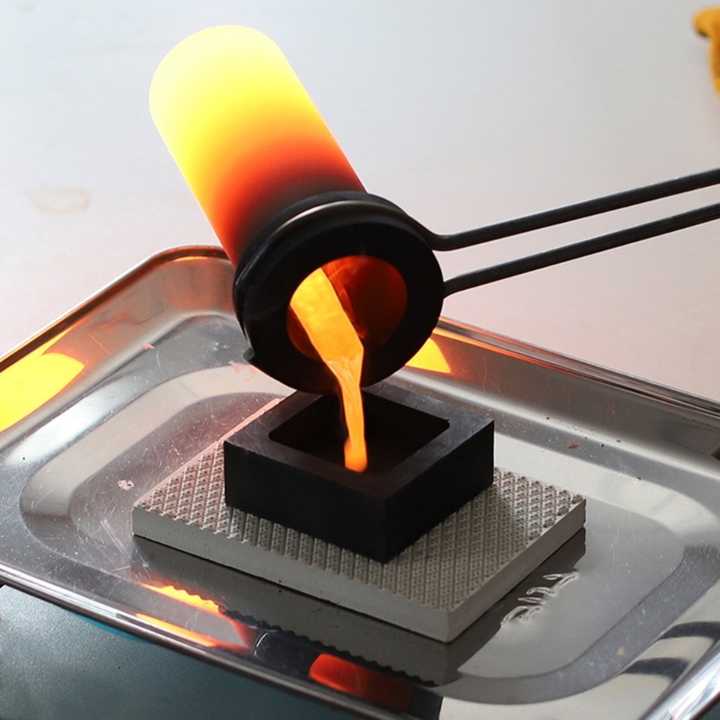
Casting and Cooling
Once the smelting process is complete, the molten metal needs to be cast into usable forms and cooled.
Pouring
The molten metal is poured into molds to create ingots, bars, or other shapes. This step must be done carefully to ensure that the metal solidifies properly and maintains its desired shape.
Cooling
The cast metal is allowed to cool and solidify. Cooling must be controlled to prevent defects and ensure the metal’s structural integrity.
Post-Smelting Treatments
After casting, additional treatments may be required to further refine the metal or prepare it for specific applications.
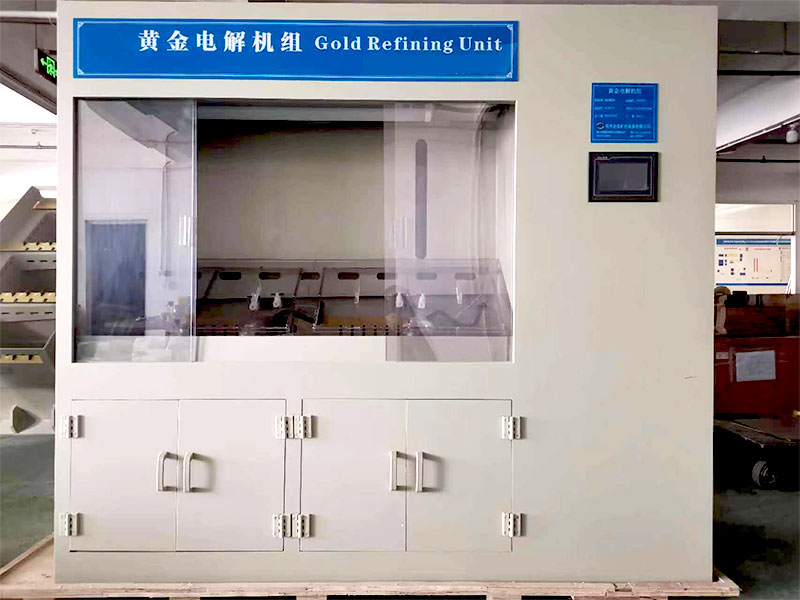
Assaying
Assaying is performed to determine the purity of the metal. This is done using various analytical techniques to confirm that the metal meets industry standards.
Surface Treatment
Depending on its intended use, the metal may undergo surface treatments, such as polishing or coating, to enhance its appearance and properties.
Equipment Used in the Precious Metal Smelting Process
The precious metal smelting process relies on specialized equipment to achieve high efficiency and quality. Key equipment includes:
Smelting Furnaces
Smelting furnaces are crucial for heating and melting the raw materials. Different types of furnaces are used based on the requirements of the process.
Electric Furnaces
Electric furnaces use electrical energy to reach the high temperatures needed for smelting. They are known for their precision and efficiency.
Blast Furnaces
Blast furnaces are used for larger-scale operations and can handle high volumes of material. They use a combination of air and fuel to achieve the necessary temperatures.
Crucibles and Molds
Crucibles are used to hold the molten metal during the smelting process, while molds shape the metal once it is poured.
Graphite Crucibles
Graphite crucibles are popular for their ability to withstand high temperatures and resist chemical reactions with molten metals.
Metal Molds
Metal molds are used to cast the molten metal into various shapes, such as ingots or bars.
Analytical Equipment
Analytical equipment is used to test the purity of the metal and ensure it meets industry standards.
Spectrometers
Spectrometers are used to analyze the metal’s composition and determine its purity.
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Analyzers
XRF analyzers provide rapid and non-destructive analysis of metal samples to assess their purity.
Best Practices for the Precious Metal Smelting Process
To achieve optimal results in the precious metal smelting process, certain best practices should be followed.
Maintaining Equipment
Regular maintenance of smelting equipment is essential for ensuring its efficiency and longevity.
Routine Inspections
Conduct routine inspections of furnaces, crucibles, and other equipment to identify and address any issues before they affect the smelting process.
Proper Cleaning
Clean equipment thoroughly after each use to prevent contamination and maintain optimal performance.
Monitoring the Process
Accurate monitoring of the smelting process is crucial for achieving high-quality results.
Temperature Control
Maintain precise temperature control throughout the smelting process to ensure consistent results and prevent overheating or underheating.
Flux Management
Properly manage flux additions to optimize the separation of impurities and improve the quality of the final product.
Ensuring Safety
Safety is paramount in the smelting process due to the high temperatures and potentially hazardous materials involved.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wear appropriate PPE, including heat-resistant gloves, safety goggles, and protective clothing, to safeguard against heat and molten metal.
Safety Protocols
Follow established safety protocols to minimize risks and ensure a safe working environment.
The precious metal smelting process is a complex and critical procedure for refining and purifying valuable metals. By understanding the stages of the process, the equipment used, and best practices for operation, you can ensure efficient and high-quality results. Whether for industrial applications or smaller-scale projects, mastering the smelting process is essential for achieving the desired purity and quality of precious metals.