scrap gold refining
Scrap gold refining is a crucial process that allows for the recovery and purification of gold from various sources, such as old jewelry, electronic waste, and industrial by-products. As gold prices fluctuate and environmental concerns rise, the importance of refining scrap gold continues to grow. This article delves into the techniques used in scrap gold refining, the essential steps involved, and the broader impact on the industry.
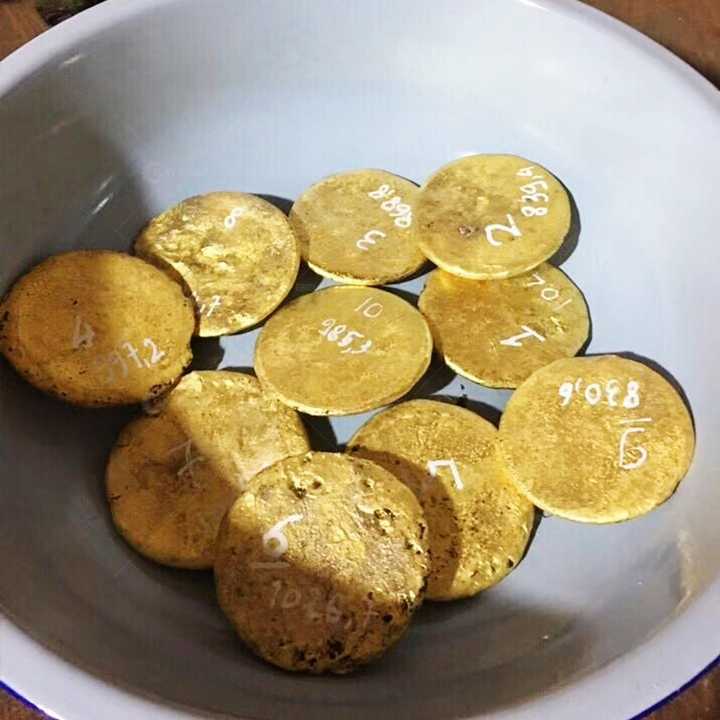

Techniques Used in Scrap Gold Refining
Scrap gold refining involves various techniques to extract and purify gold from discarded materials. These methods ensure that the gold is recovered efficiently and meets the required purity standards.
- Miller Process:
- The Miller process is one of the traditional methods used in scrap gold refining. It involves introducing chlorine gas into molten gold, which reacts with impurities to form chlorides that can be easily removed. This technique is relatively fast and cost-effective, making it suitable for refining large quantities of scrap gold. However, it typically produces gold with a purity of about 99.5%, which may not be sufficient for all applications.
- Aqua Regia Process:
- The aqua regia process is widely used in scrap gold refining, particularly for smaller batches of gold or for gold that needs to be refined to a higher purity level. Aqua regia, a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, dissolves gold and separates it from other metals. This method is versatile and can be used to refine gold to a high degree of purity, though it requires careful handling due to the corrosive nature of the chemicals involved.
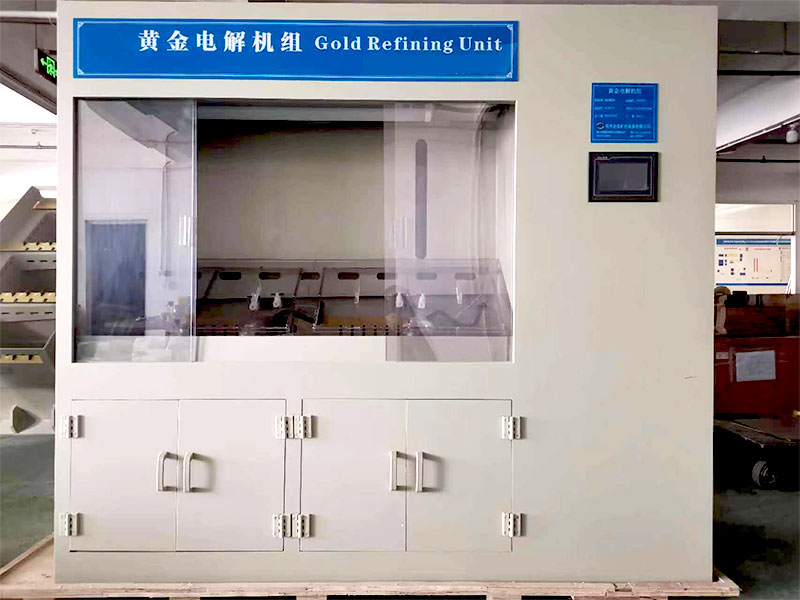
- Electrolytic Refining:
- For the highest levels of purity, electrolytic refining is often employed in scrap gold refining. This method involves dissolving gold in an acidic solution and passing an electric current through the solution. Pure gold is deposited onto the cathode, while impurities are left behind. Electrolytic refining can produce gold with a purity of up to 99.99%, making it ideal for applications requiring ultra-pure gold.
- Cupellation:
- Cupellation is a more ancient technique used in the refining of scrap gold, particularly when the gold is alloyed with lead or other metals. The process involves heating the scrap material in a furnace, where lead oxidizes and separates from the gold. While not as commonly used today, cupellation remains a valuable technique in specific scenarios.
Key Steps in Scrap Gold Refining
The process of scrap gold refining involves several key steps that ensure the efficient recovery and purification of gold.
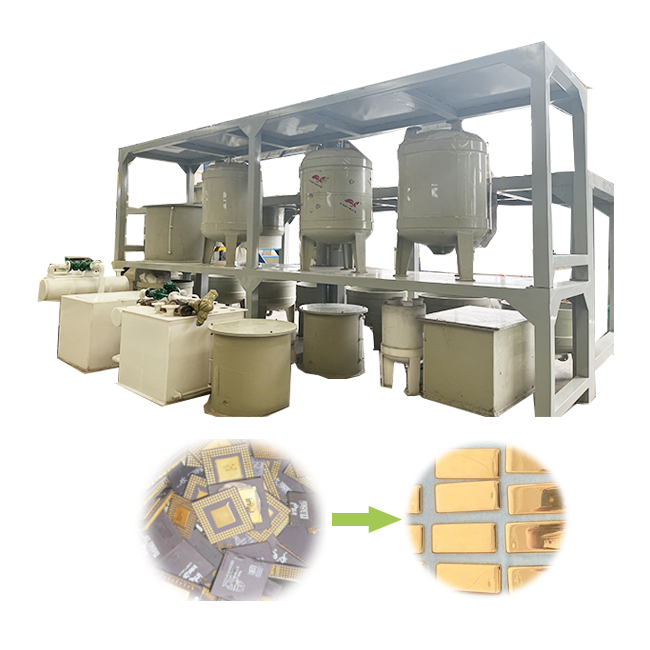
- Collection and Sorting:
- The first step in scrap gold refining is collecting and sorting the scrap materials. This can include anything from old jewelry and dental crowns to electronic components and industrial scrap. The materials are then sorted based on their gold content and the presence of other metals or contaminants.
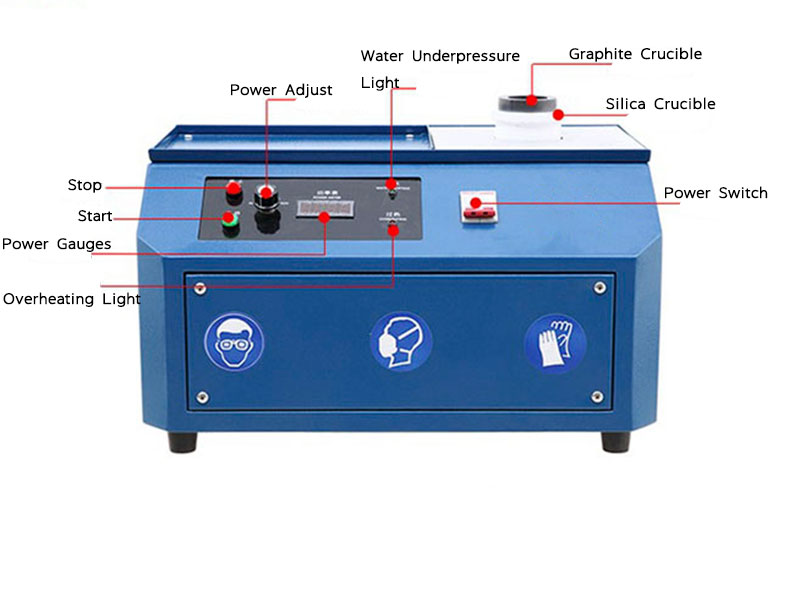
- Melting and Sampling:
- Once the scrap gold is collected, it is melted in a high-temperature furnace. This allows for sampling to determine the exact composition of the material and to select the most appropriate refining technique. The melting process also helps in removing some of the base metals and other impurities.
- Preliminary Refining:
- In many cases, preliminary refining is necessary to remove non-gold metals from the scrap material. This step often involves the use of fluxes and other chemicals that bind with the impurities, allowing them to be separated from the gold during the melting process.
- Chemical Treatment:
- After preliminary refining, the gold undergoes chemical treatment, where it is dissolved in acids such as aqua regia. This step is critical for separating the gold from any remaining impurities and other metals.
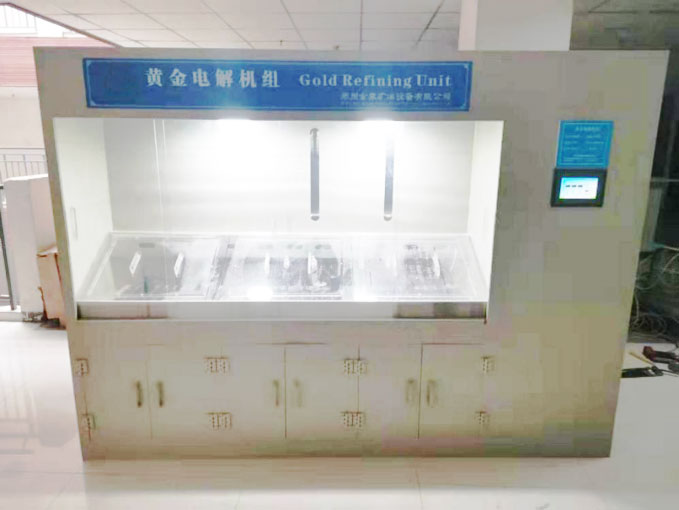
- Electrolytic Refining:
- For scrap gold that needs to be refined to the highest purity, electrolytic refining is employed. This process involves passing an electric current through a gold-containing solution, causing pure gold to deposit onto a cathode. The result is gold of exceptional purity, suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Filtration and Washing:
- After the refining process, the gold is filtered and washed to remove any residual chemicals. This ensures that the final product is free of contaminants and meets the required purity standards.
- Casting and Final Inspection:
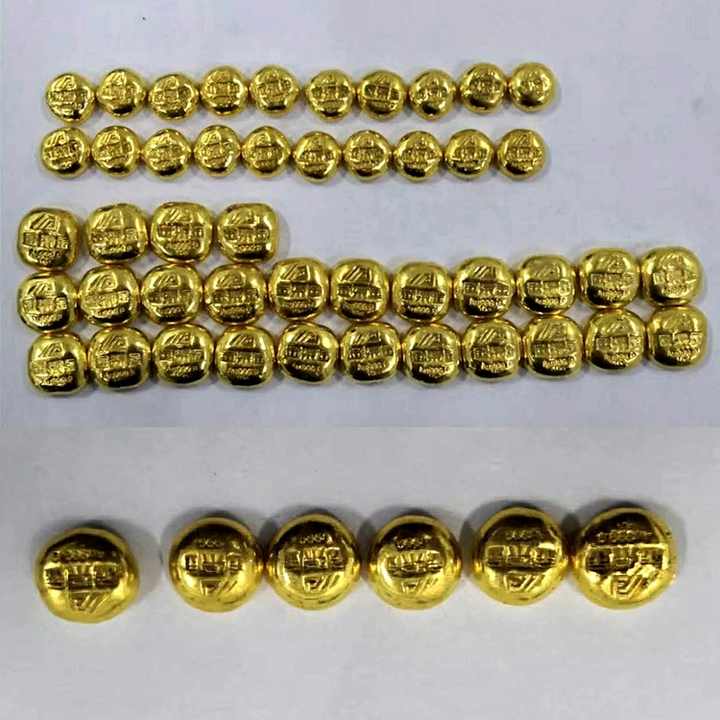
- The refined gold is then melted once more and cast into bars, ingots, or other forms as required. The final product is inspected for weight, purity, and appearance before it is ready for sale or further use.
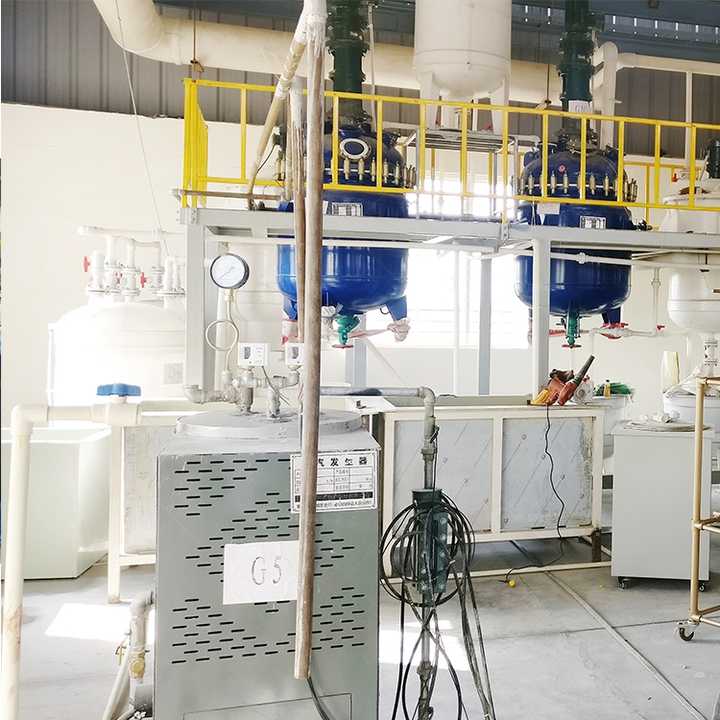
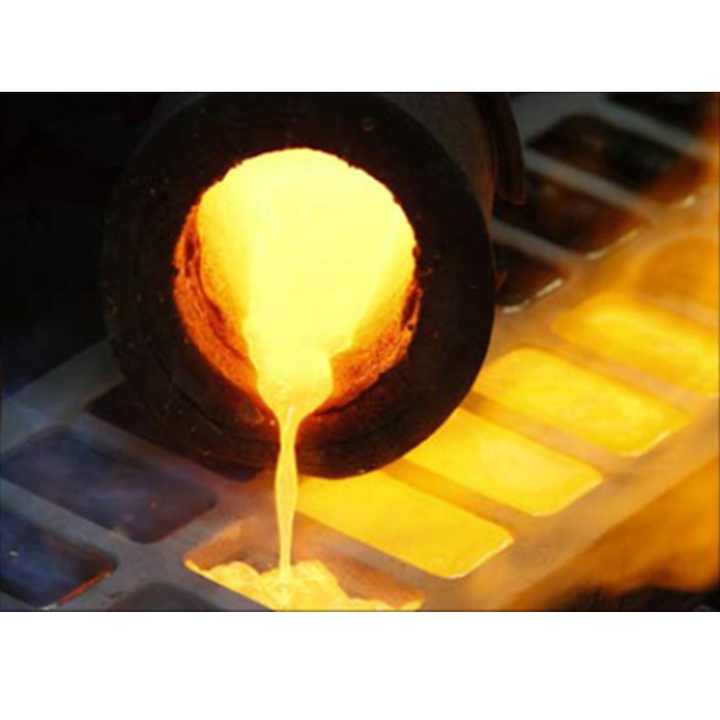
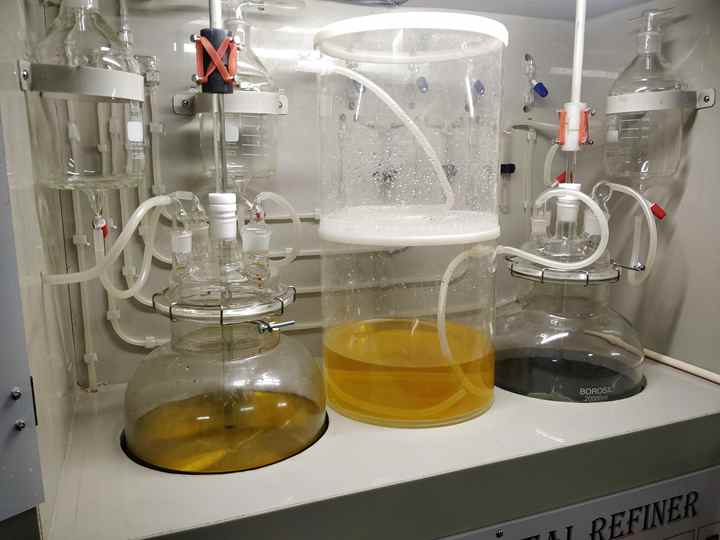



The Industry Impact of Scrap Gold Refining
Scrap gold refining plays a significant role in the gold industry, providing both economic and environmental benefits.
- Economic Value:
- The economic value of scrap gold refining is substantial. By recovering gold from scrap materials, refiners can reduce the need for new gold mining, which is costly and environmentally destructive. The recycled gold can be reintroduced into the market, providing a steady supply for industries such as jewelry, electronics, and finance.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Refining scrap gold is far more environmentally friendly than traditional gold mining. Mining operations require significant land disruption and generate large amounts of waste and pollution. In contrast, refining scrap gold uses existing materials, reducing the environmental impact and contributing to more sustainable practices within the industry.
- Meeting Industry Demand:
- The demand for gold continues to rise, driven by its use in various industries. Scrap gold refining helps meet this demand by providing a reliable source of high-purity gold. This is particularly important for industries that require gold with specific purity levels, such as electronics and medical devices.
- Supporting the Circular Economy:
- Scrap gold refining is a key component of the circular economy, where materials are reused and recycled rather than discarded. By refining gold from scrap, the industry reduces waste and maximizes the use of resources, supporting long-term sustainability.


Scrap gold refining is a critical process that enables the recovery and purification of gold from a wide range of sources. Through various techniques, such as the Miller process, aqua regia, and electrolytic refining, refiners can achieve high levels of purity, ensuring that the gold is suitable for various applications. The process not only provides economic value and meets industry demand but also offers significant environmental benefits by reducing the need for new gold mining. As the industry continues to evolve, scrap gold refining will remain an essential part of the global gold supply chain.