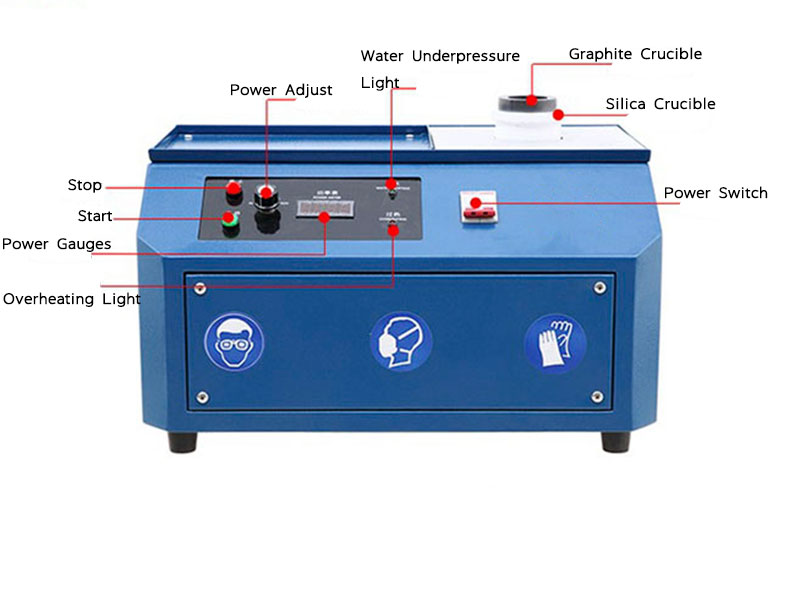
steps of purification of gold
Understanding the Steps of Purification of Gold
Gold is one of the most sought-after metals due to its beauty, rarity, and unique properties. However, gold in its raw form is often mixed with other metals and impurities. To obtain pure gold, a series of refining steps must be undertaken. The steps of purification of gold involve various techniques to remove impurities, leaving behind high-quality, pure gold. This article will explore the key steps involved in this process, explaining each method and its role in achieving the desired level of purity.
The Importance of Gold Purification
Purifying gold is essential for several industries, including jewelry, electronics, and financial markets. Impure gold, while still valuable, lacks the brilliance and conductivity required for these industries. Therefore, understanding the steps of purification of gold is critical to maximizing the utility and value of this precious metal.
Gold purification not only improves the metal’s aesthetic and functional qualities but also helps ensure that it meets specific industry standards. Whether for investment, craftsmanship, or industrial purposes, gold must undergo a purification process to meet these high demands.
Key Steps of Purification of Gold
Initial Screening and Crushing
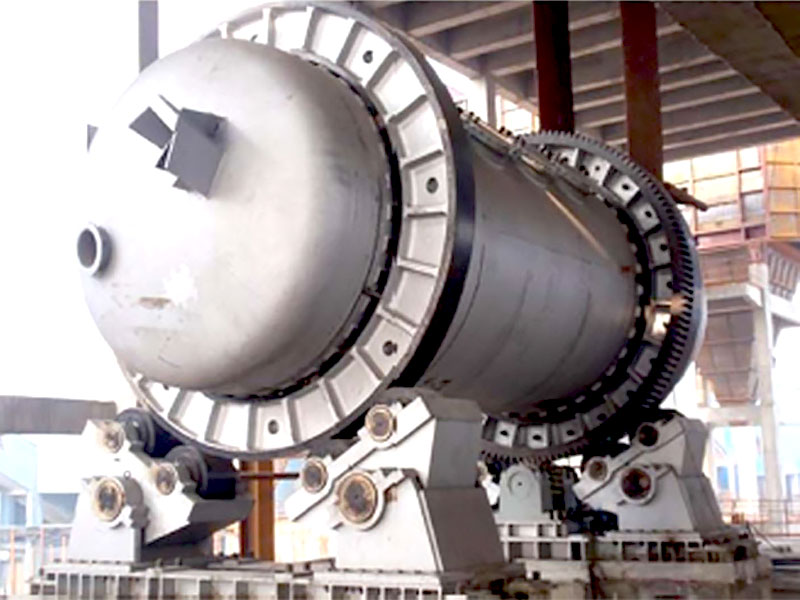
The first step in the steps of purification of gold is the initial screening and crushing of the raw gold ore. Gold is typically found mixed with other metals like silver, copper, and zinc. To begin the refining process, the ore must be broken down into smaller particles. This allows the valuable gold to be separated from the surrounding rock.
- Process: The ore is crushed into fine powder using mechanical crushers. Once the ore is finely crushed, it undergoes screening to remove larger rocks and debris.
- Purpose: This step prepares the gold for further chemical or physical purification processes by making it easier to separate from impurities.
Gravity Separation
Once the ore has been crushed, one of the oldest methods used in the steps of purification of gold is gravity separation. This method takes advantage of the higher density of gold compared to other materials in the ore.
- Process: Gold is separated from lighter materials like sand and gravel by using gravity. The gold particles settle at the bottom, while lighter materials are washed away. This process can be done using sluices, shaking tables, or jigs.
- Purpose: Gravity separation is an effective first step to concentrate the gold before moving on to more complex purification methods.
Amalgamation
Amalgamation is another common step used in the steps of purification of gold, especially in small-scale operations. In this process, mercury is used to extract gold from the ore.
- Process: The crushed ore is mixed with mercury, forming an amalgam with the gold. The mercury is then heated and evaporates, leaving behind pure gold.
- Purpose: While amalgamation is an effective method for extracting gold, it has environmental and health concerns due to the use of mercury.
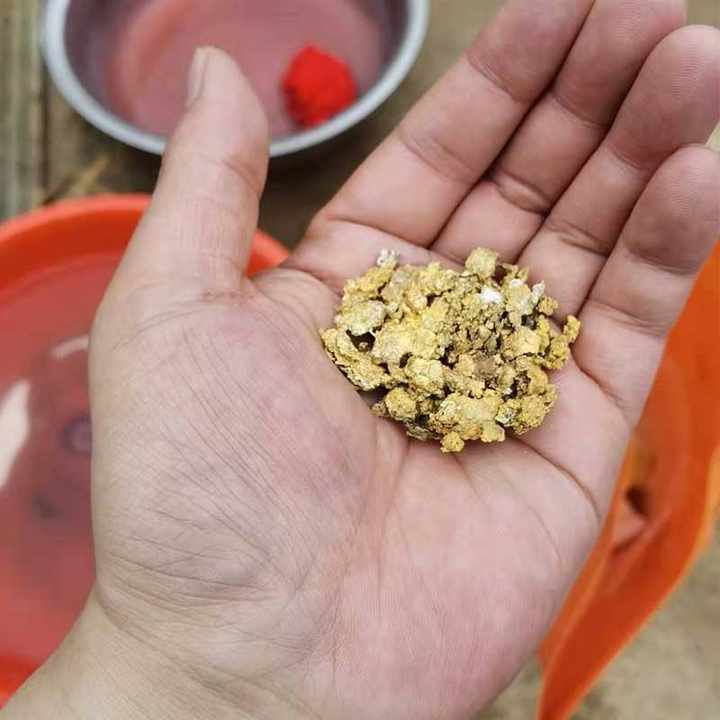
Chemical Leaching
Chemical leaching is one of the more advanced steps of purification of gold and is used to refine gold on a larger scale. This method dissolves gold from the ore using a chemical solution, most commonly cyanide or aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid).
- Process: In cyanide leaching, the ore is treated with a cyanide solution, which dissolves the gold. The gold is then precipitated out of the solution using zinc or activated carbon. In aqua regia leaching, gold is dissolved in the acid mixture and later recovered through precipitation.
- Purpose: Chemical leaching is highly efficient and can purify gold to extremely high levels. It is the preferred method for large-scale gold refining operations.
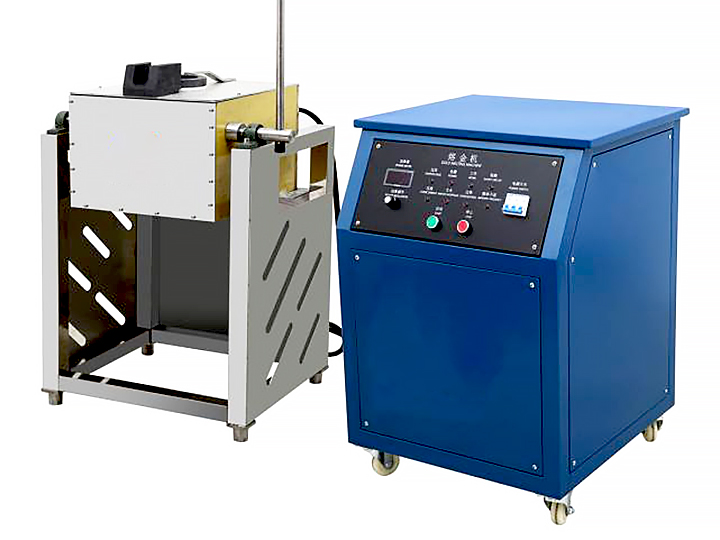
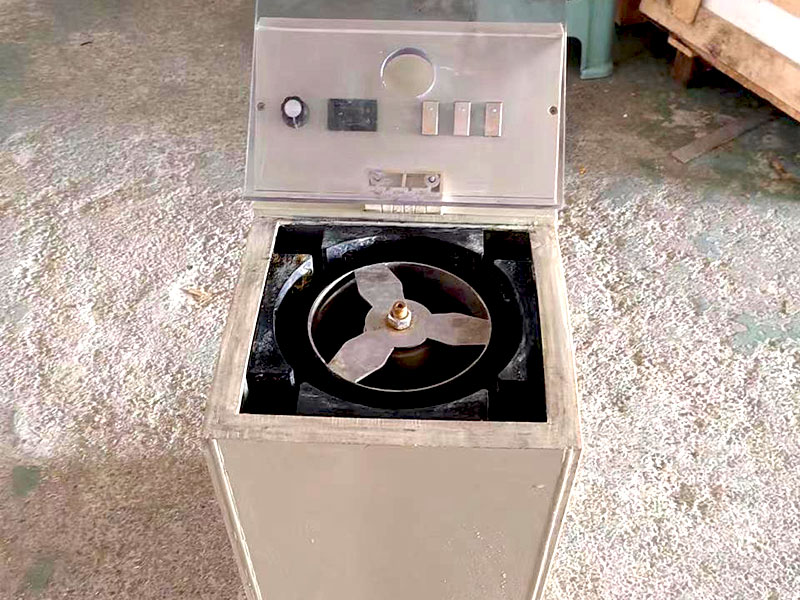
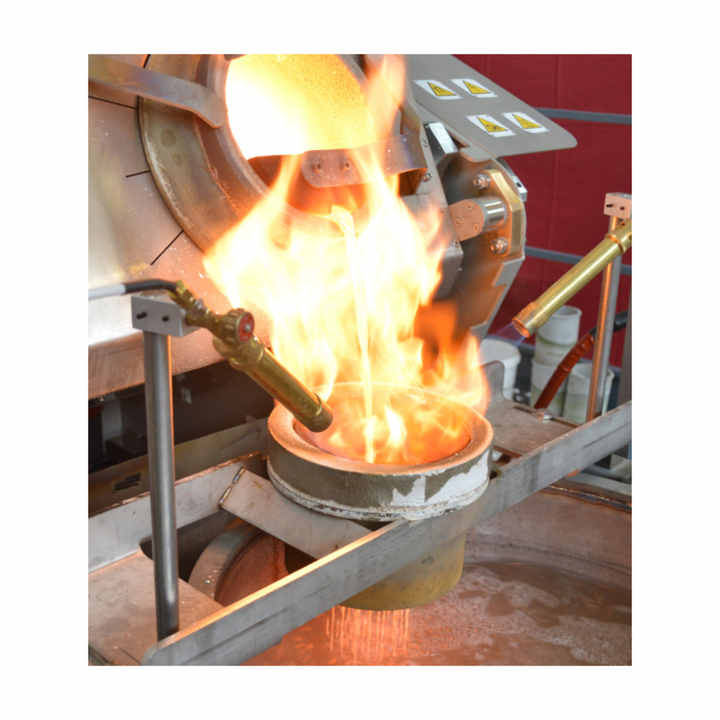
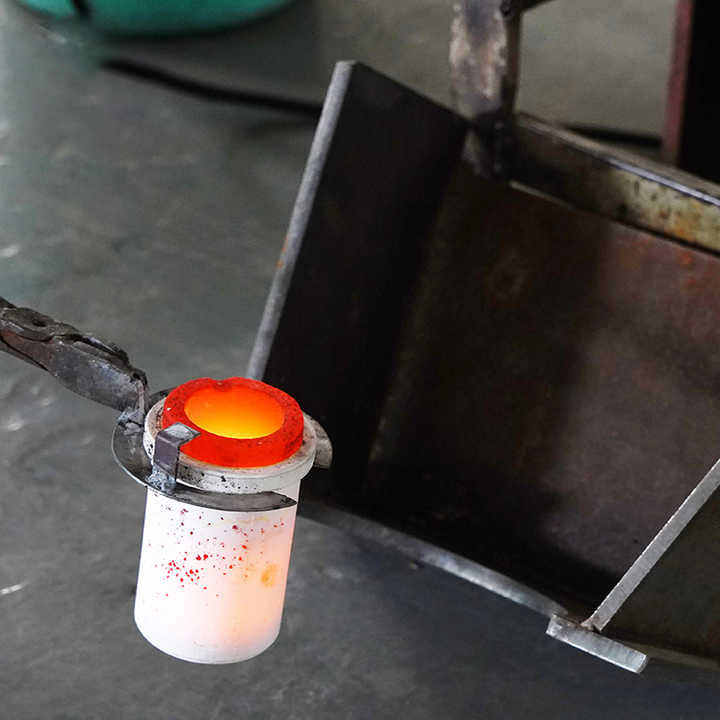
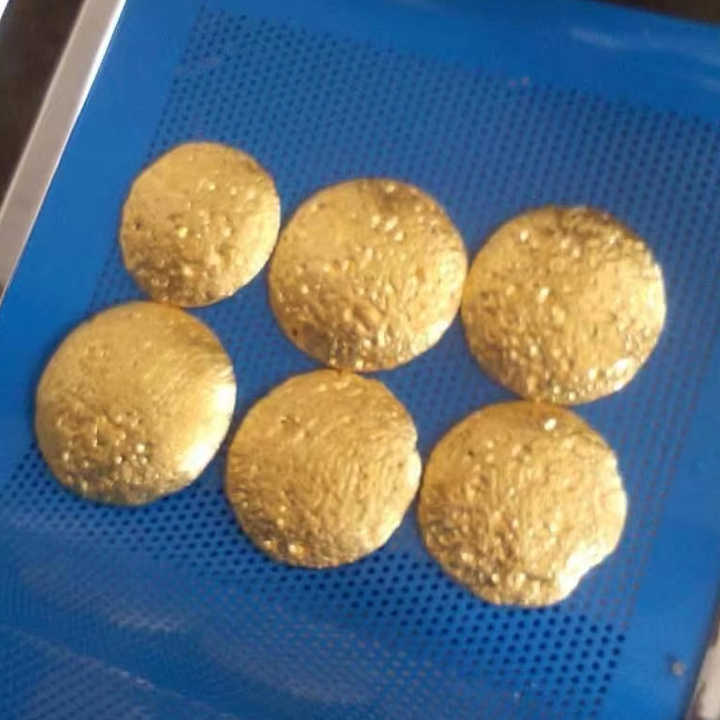
Smelting
Smelting is a crucial step in the steps of purification of gold, where the gold is heated to a high temperature in a furnace. This method helps separate gold from impurities and other metals that may still be present.
- Process: Gold is placed in a furnace and heated to its melting point. During this process, fluxes like borax are added to bind with impurities, forming slag. The pure gold sinks to the bottom of the furnace, while the slag is removed.
- Purpose: Smelting produces highly purified gold and is often the final step before further refinement or molding into bars and coins.
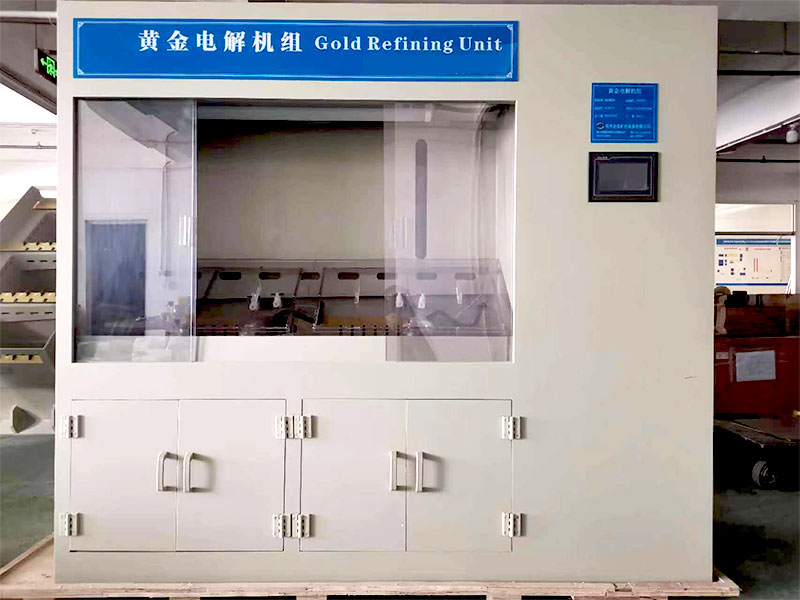
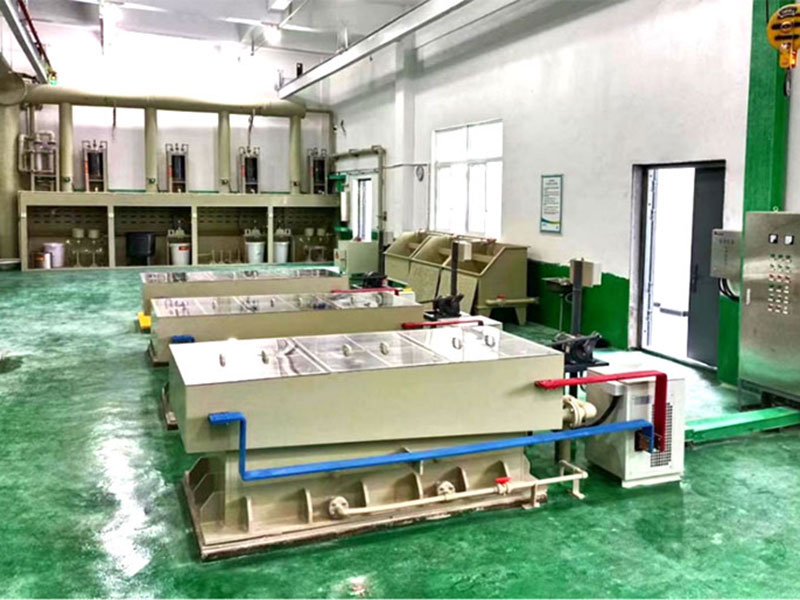
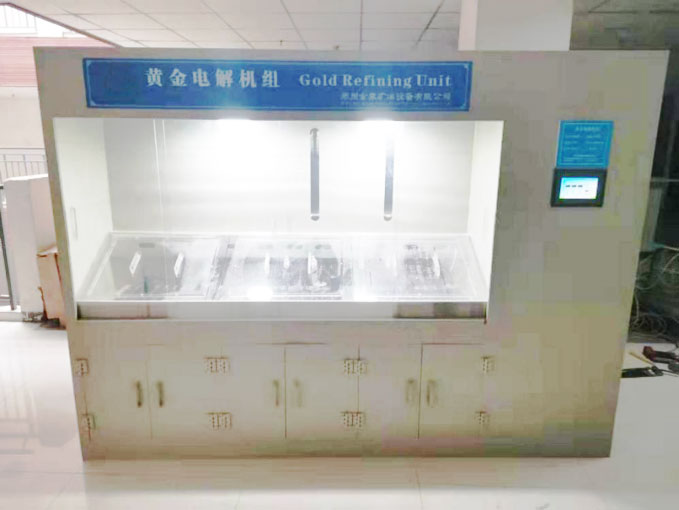
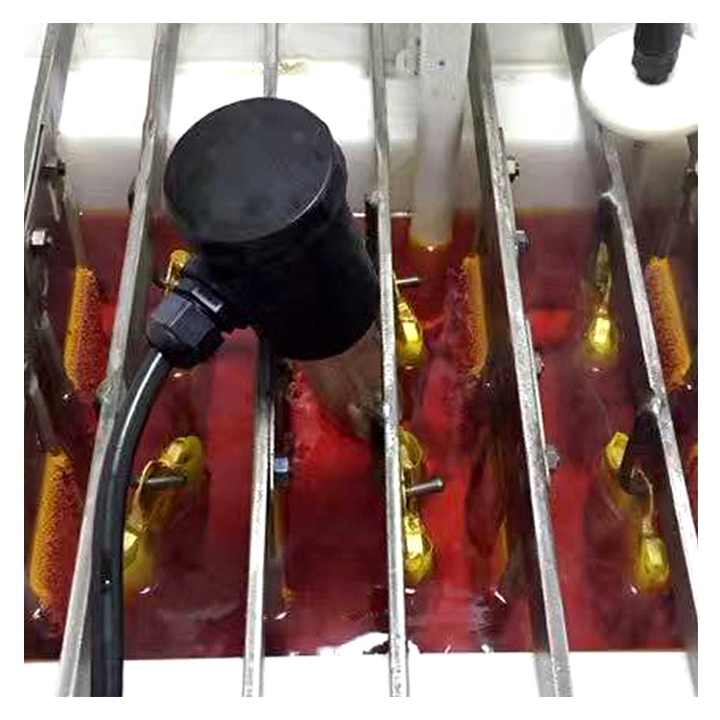
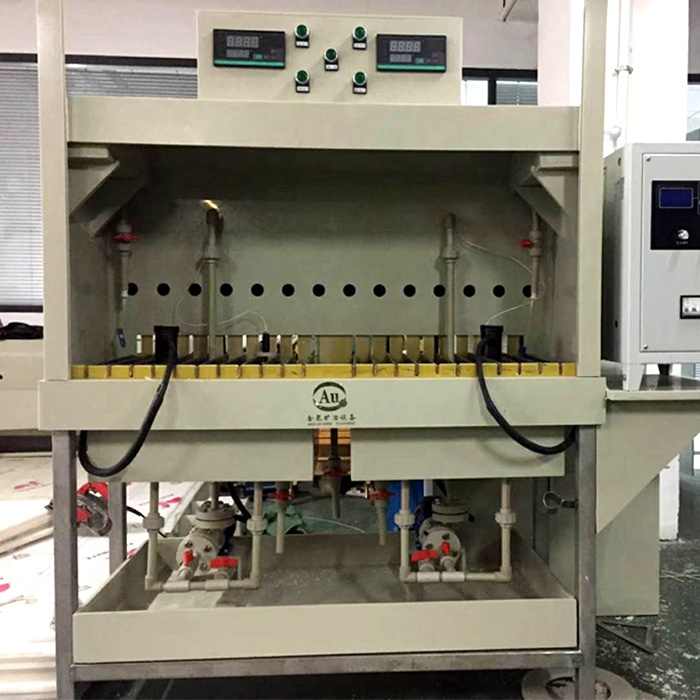
Electrolytic Refining
For achieving extremely high levels of purity, electrolytic refining is one of the final steps of purification of gold. This method involves the use of an electrical current to further refine gold.
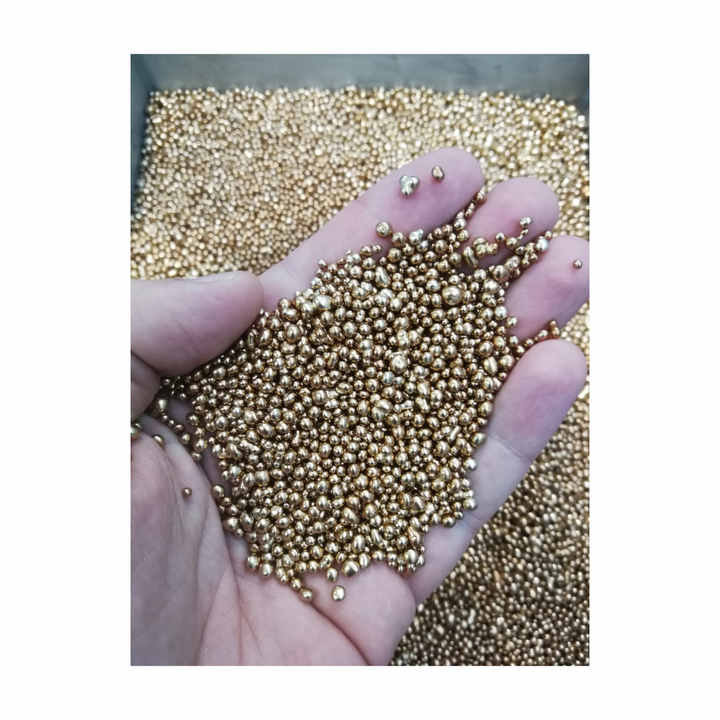
- Process: Gold is placed in an electrolyte solution, and an electric current is passed through it. The gold dissolves into the solution and is deposited onto a cathode as pure gold. Impurities are left behind in the solution or form a sludge.
- Purpose: Electrolytic refining can produce gold of 99.999% purity, making it one of the most effective techniques for purifying gold.
Environmental Considerations in the Purification Process
While the steps of purification of gold are necessary for producing high-purity metal, some processes have environmental impacts. For instance, chemical leaching methods like cyanide and aqua regia can generate hazardous waste. Proper waste management and recycling of chemicals are essential to minimize environmental damage.
Additionally, the energy consumption in smelting and electrolytic refining processes can be significant. However, advancements in technology and sustainable practices are helping to reduce the environmental footprint of gold purification.
Conclusion
The steps of purification of gold are varied and complex, each playing a critical role in producing the highest quality metal. From initial crushing and screening to advanced techniques like electrolytic refining, each step helps remove impurities and increase the gold’s value. As technology evolves, these processes are becoming more efficient, reducing costs and environmental impact, while still producing the purest gold possible. Understanding these steps provides insight into the fascinating journey of gold from raw ore to the highly sought-after precious metal used in various industries around the world.